What Do You Call The System That Collects Taxes To Pay For Social Services
What You'll Learn
- Discover the three basic tax types—taxes on what you earn, taxes on what you buy, and taxes on what you own.
- Learn about 12 specific taxes, iv inside each principal category—earn: individual income taxes, corporate income taxes, payroll taxes, and upper-case letter gains taxes; purchase: sales taxes, gross receipts taxes, value-added taxes, and excise taxes; and own: property taxes, tangible personal belongings taxes, manor and inheritance taxes, and wealth taxes.
- Develop a basic understanding of how these taxes fit together, how they impact government revenues and the economy, and where you may come across them in your daily life.
Introduction
Most taxes can be divided into three buckets: taxes on what you earn, taxes on what you buy, and taxes on what you own.
It'southward of import to remember that every dollar yous pay in taxes starts as a dollar earned every bit income. Ane of the principal differences amongst the tax types outlined beneath is the point of collection—in other words, when yous pay the tax.
For example, if yous earn $1,000 in a state with a apartment income taxation rate of 10%, $100 in income taxes should be withheld from your paycheck when you earn that income.
If, a week later on, you take $100 from your remaining earnings to buy a new smartwatch in a jurisdiction with a v% sales tax, you'll pay an boosted $v in taxes when you lot purchase that item.
Altogether, $105 of your initial $1,000 in income has been collected in taxes, just non at the same time.
With that in mind, beneath is a brief overview of the main types of taxes you should know to be an educated taxpayer.
Taxes on What You Earn
Private Income Taxes
An individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns.
Many private income taxes are "progressive," meaning tax rates increment as a taxpayer's income increases, resulting in higher-earners paying a larger share of income taxes than lower-earners.

The U.South., for example, levies income tax rates ranging from ten pct to 37 percentage that boot in at specific income thresholds outlined below. The income ranges for which these rates utilise are chosen revenue enhancement brackets. All income that falls inside each subclass is taxed at the corresponding rate.
| Rate | For Single Individuals, Taxable Income Over | For Married Individuals Filing Joint Returns, Taxable Income Over | For Heads of Households, Taxable Income Over |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| 12% | $nine,875 | $19,750 | $14,100 |
| 22% | $40,125 | $80,250 | $53,700 |
| 24% | $85,525 | $171,050 | $85,500 |
| 32% | $163,300 | $326,600 | $163,300 |
| 35% | $207,350 | $414,700 | $207,350 |
| 37% | $518,400 | $622,050 | $518,400 |
| Source: Internal Revenue Service | |||
Corporate Income Taxes
A corporate income taxation (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on concern profits, which are revenues (what a concern makes in sales) minus costs (the cost of doing business).
Businesses in U.Southward. broadly fall into 2 categories: C corporations, which pay the corporate income tax, and passthroughs—such as partnerships, S corporations, LLCs, and sole proprietorships—which "laissez passer" their income "through" to their owner's income tax returns and pay the private income tax.
While C corporations are required to pay the corporate income tax, the burden of the revenue enhancement falls not but on the business but also on its consumers and employees through higher prices and lower wages.
Due to their negative economic effects, over time, more countries take shifted to taxing corporations at rates lower than 30 percent, including the Us, which lowered its federal corporate income tax rate to 21 percent equally part of the Revenue enhancement Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.

Payroll Taxes
Payroll taxes are taxes paid on the wages and salaries of employees to finance social insurance programs. Most taxpayers will be familiar with payroll taxes from looking at their paystub at the end of each pay menstruation, where the amount of payroll tax withheld by their employer from their income is clearly listed.
In the U.S., the largest payroll taxes are a 12.four percent tax to fund Social Security and a 2.nine percent tax to fund Medicare, for a combined rate of fifteen.3 per centum. Half of payroll taxes (seven.65 percent) are remitted directly by employers, with the other half withheld from employees' paychecks.
Though roughly half of the payroll taxes are paid by employers, the economic brunt of payroll taxes is mostly borne past workers in the form of lower wages.
Capital Gains Taxes
Capital assets generally include everything owned and used for personal purposes, pleasure, or investment, including stocks, bonds, homes, cars, jewelry, and art. Whenever one of those assets increases in value—east.g., when the cost of a stock you lot own goes upwards—the result is what's called a "capital proceeds."
In jurisdictions with a capital gains tax, when a person "realizes" a majuscule gain—i.e., sells an asset that has increased in value—they pay tax on the profit they earn.
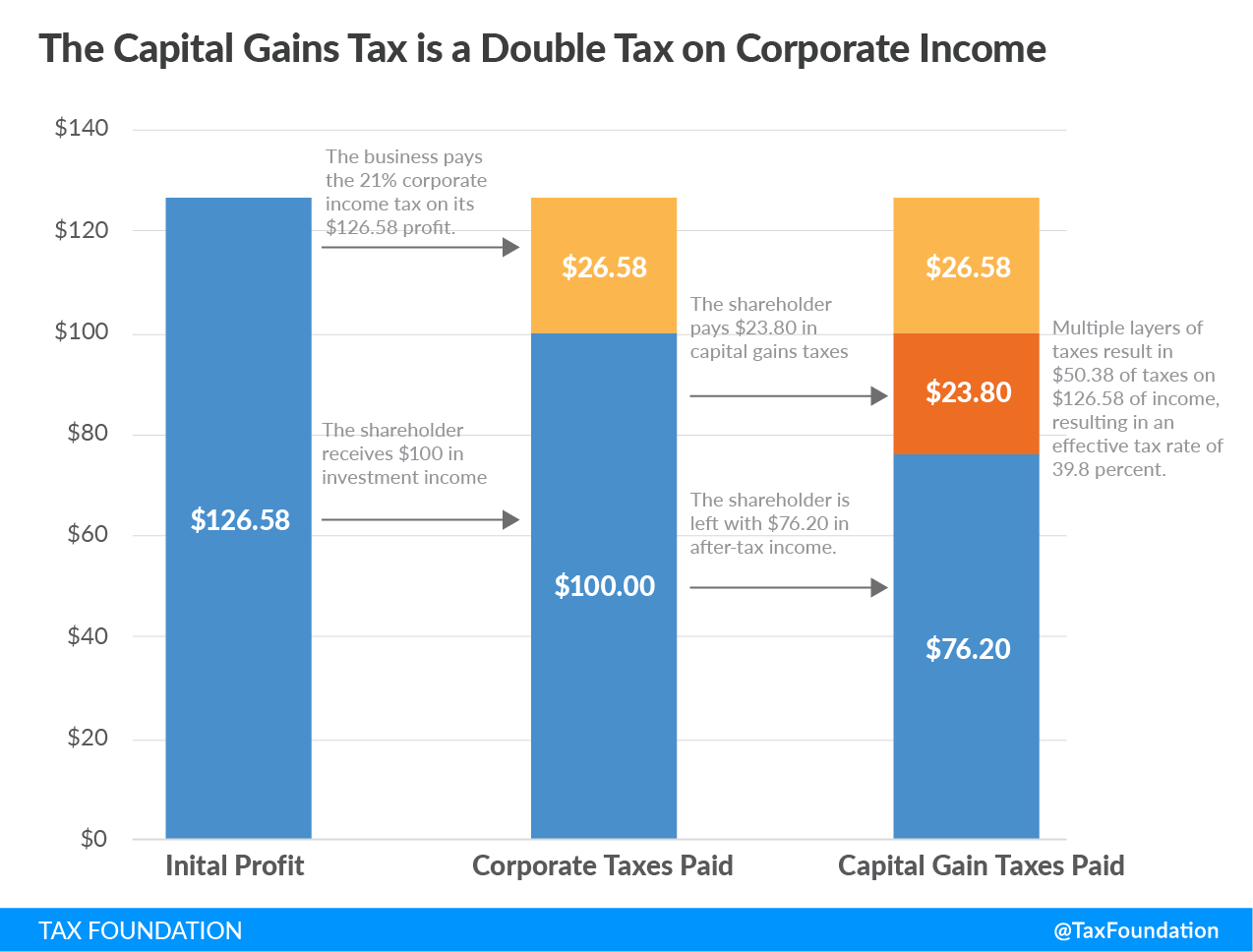
When applied to profits earned from stocks, capital gains taxes result in the same dollar being taxed twice, also known as double taxation. That's because corporate earnings are already subject to the corporate income revenue enhancement.
Taxes on What You Buy
Sales Taxes
Sales taxes are a form of consumption tax levied on retail sales of goods and services. If you live in the U.S., you are probable familiar with the sales tax from having seen it printed at the bottom of shop receipts.
The U.S. is one of the few industrialized countries that even so relies on traditional retail sales taxes, which are a meaning source of state and local revenue. All U.S. states other than Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon collect statewide sales taxes, as exercise localities in 38 states.
Sales tax rates can take a pregnant touch on on where consumers cull to shop, merely the sales revenue enhancement base—what is and is not subject to sales tax—also matters. Tax experts recommend that sales taxes apply to all appurtenances and services that consumers purchase merely non to those that businesses purchase when producing their own appurtenances.
Gross Receipts Taxes
Gross receipts taxes (GRTs) are applied to a company's gross sales, regardless of profitability and without deductions for business concern expenses. This is a key deviation from other taxes businesses pay, such as those based on profits or net income, like a corporate income revenue enhancement, or concluding consumption, similar a well-constructed sales taxation.
Because GRTs are imposed at each stage in the product chain, they result in "revenue enhancement pyramiding," where the tax burden multiplies throughout the production chain and is eventually passed on to consumers.
GRTs are especially harmful for startups, which post losses in early on years, and businesses with long production chains. Despite being dismissed for decades as inefficient and unsound taxation policy, policymakers have recently begun considering GRTs once more every bit they seek new acquirement streams.
Value-Added Taxes
A Value-Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption taxation assessed on the value added in each production stage of a skilful or service.
Each business organisation along the production concatenation is required to pay a VAT on the value of the produced good/service at that phase, with the VAT previously paid for that good/service beingness deductible at each footstep.
The final consumer, however, pays the VAT without being able to deduct the previously paid VAT, making information technology a revenue enhancement on terminal consumption. This system ensures that only final consumption can be taxed nether a VAT, avoiding taxation pyramiding.
More than 140 countries worldwide and all OECD countries except the Us levy a VAT, making it a significant revenue source and the almost common form of consumption taxation globally.
Excise Taxes
Excise taxes are taxes imposed on a specific good or activeness, unremarkably in add-on to a broad consumption tax, and comprise a relatively small and volatile share of total tax collections. Common examples of excise taxes include those on cigarettes, booze, soda, gasoline, and betting.
Excise taxes can be employed every bit "sin" taxes, to offset externalities. An externality is a harmful side effect or event non reflected in the cost of something. For instance, governments may place a special tax on cigarettes in hopes of reducing consumption and associated health-care costs, or an boosted tax on carbon to curb pollution.
Excise taxes tin also be employed as user fees. A expert example of this is the gas tax. The amount of gas a driver purchases generally reflects their contribution to traffic congestion and road wear-and-tear. Taxing this purchase effectively puts a price on using public roads.
Taxes on Things You Own
Holding Taxes
Property taxes are primarily levied on immovable holding like land and buildings and are an essential source of revenue for state and local governments in the U.S.
Belongings taxes in the U.S. account for over 30 percent of full state and local tax collections and over 70 percentage of total local revenue enhancement collections. Local governments rely on property tax revenue to fund public services similar schools, roads, police and fire departments, and emergency medical services.
While most people are familiar with residential belongings taxes on state and structures, known as "real" property taxes, many states too tax "tangible personal property" (TPP), such as vehicles and equipment owned by individuals and businesses.
Overall, taxes on real property are relatively stable, neutral, and transparent, whereas taxes on tangible personal property are more than problematic.
Tangible Personal Property (TPP) Taxes
Tangible personal property (TPP) is property that can be moved or touched, such as business equipment, mechanism, inventory, piece of furniture, and automobiles.
Taxes on TPP make upward a small share of total state and local taxation collections, but are complex, creating high compliance costs; are nonneutral, favoring some industries over others; and distort investment decisions.
TPP taxes place a brunt on many of the avails businesses use to grow and become more than productive, such as machinery and equipment. By making ownership of these assets more expensive, TPP taxes discourage new investment and have a negative affect on economical growth overall. As of 2019, 43 states taxed tangible personal property.

Estate and Inheritance Taxes
Both estate and inheritance taxes are imposed on the value of an individual's belongings at the fourth dimension of their death. While estate taxes are paid by the estate itself, before assets are distributed to heirs, inheritance taxes are paid by those who inherit property. Both taxes are ordinarily paired with a "souvenir tax" so that they cannot be avoided by transferring the property prior to death.
Manor and inheritance taxes are poor economic policy considering they fall almost exclusively on a country or state'south "capital stock"—the accumulated wealth that makes it richer and more productive as a whole—thus discouraging investment.
Both taxes are also complex, hard for jurisdictions to administer, and can incentivize high-net-worth individuals to either engage in economically inefficient estate planning or leave a land or country altogether.
For these reasons, most U.S. states accept moved away from estate and inheritance taxes.
Wealth Taxes
Wealth taxes are typically imposed annually on an individual's cyberspace wealth (full assets, minus any debts owed) to a higher place a sure threshold.
For case, a person with $2.five million in wealth and $500,000 in debt would have a net wealth of $2 one thousand thousand. If a wealth tax applies to all wealth above $i 1000000, then nether a five percent wealth taxation the individual would owe $50,000 in taxes.
Every bit of 2019, only vi countries in Europe—Norway, Spain, Switzerland, Belgium, holland, and Italy—had a wealth tax and two of those—the Netherlands and Italy—raised no revenue from it (see chart below). Countries accept repealed their wealth taxes considering they're difficult to administer, raise relatively little revenue, and can have harmful effects on the economy, including discouraging entrepreneurship and innovation.

What Do You Call The System That Collects Taxes To Pay For Social Services,
Source: https://taxfoundation.org/the-three-basic-tax-types/
Posted by: guntherthust1969.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Do You Call The System That Collects Taxes To Pay For Social Services"
Post a Comment